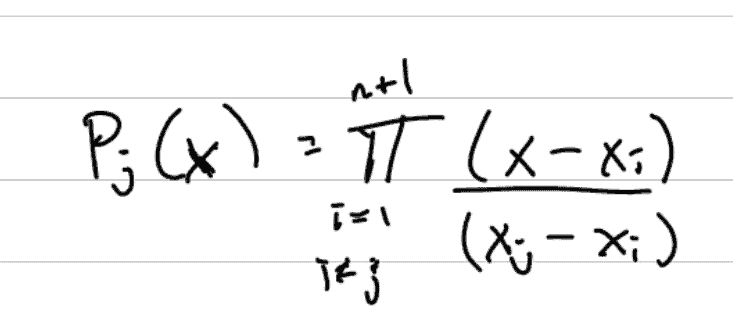
LaGrange polynomials are a funny thing, and come with a little bit of work.
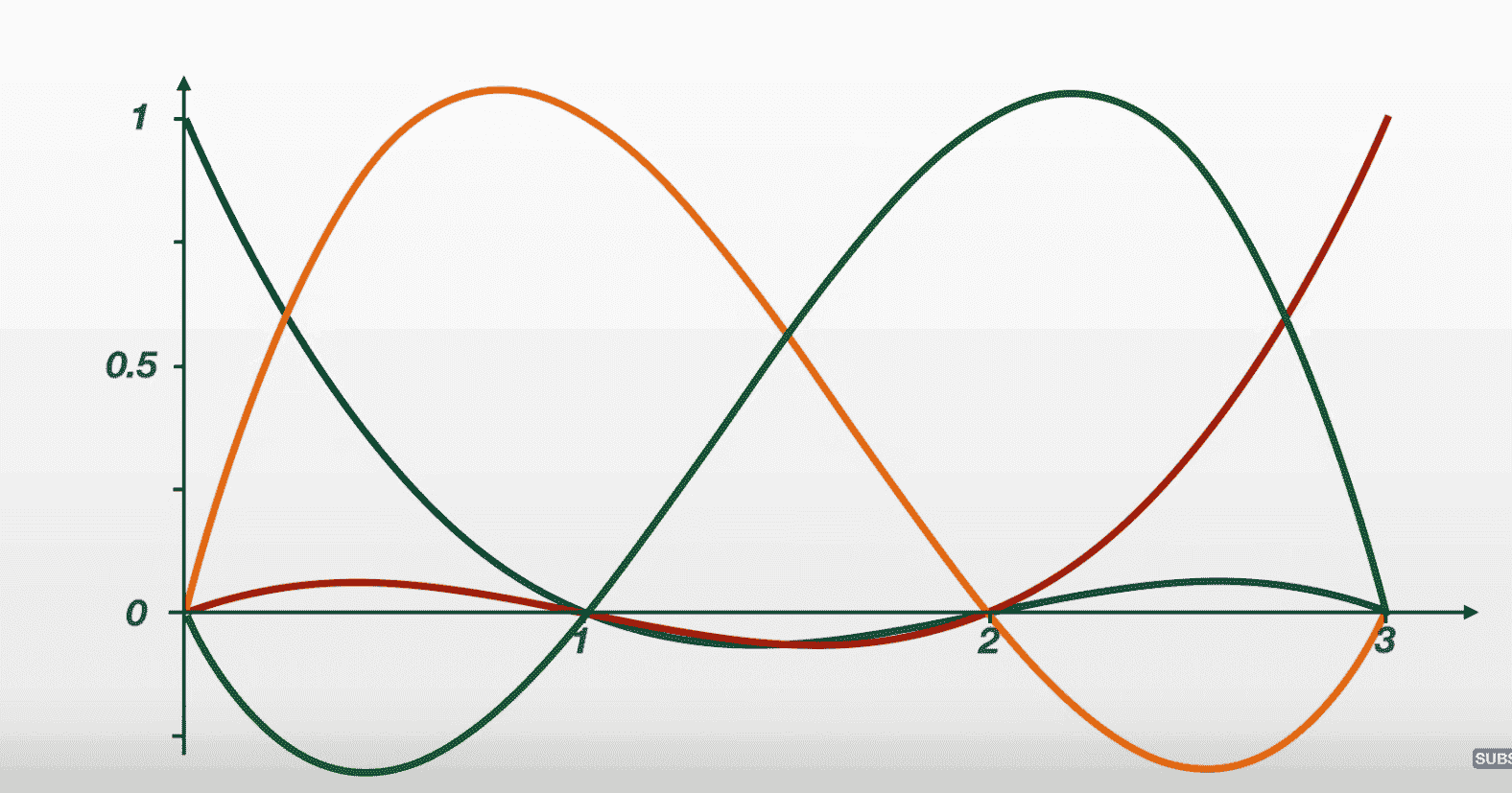
What is happening, is you are creating a polynomial for each point on the plane, and adding them all up. You can literally create the original polynomial from these other ones. Each point in the LeGrange polynomial process starts at a magnitude of one, and you multiply it by a scalar (Y value) to fit it.
- You will be given X points, and a Y = Sin(x), or (X,Y) coordinate points
- The Y value given, or found, is representative of the scalar.
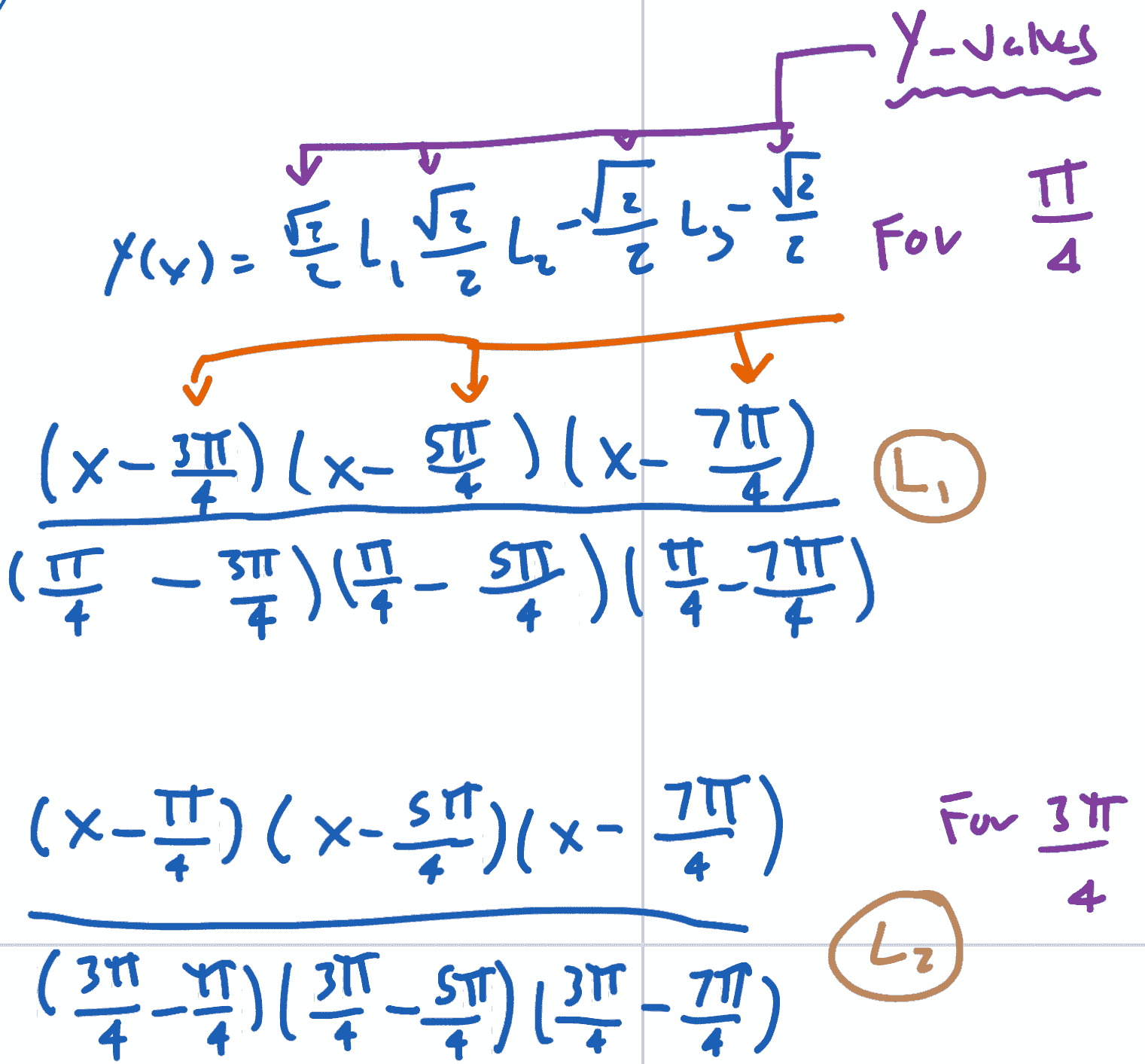
- Plug in X values like this, in this order.